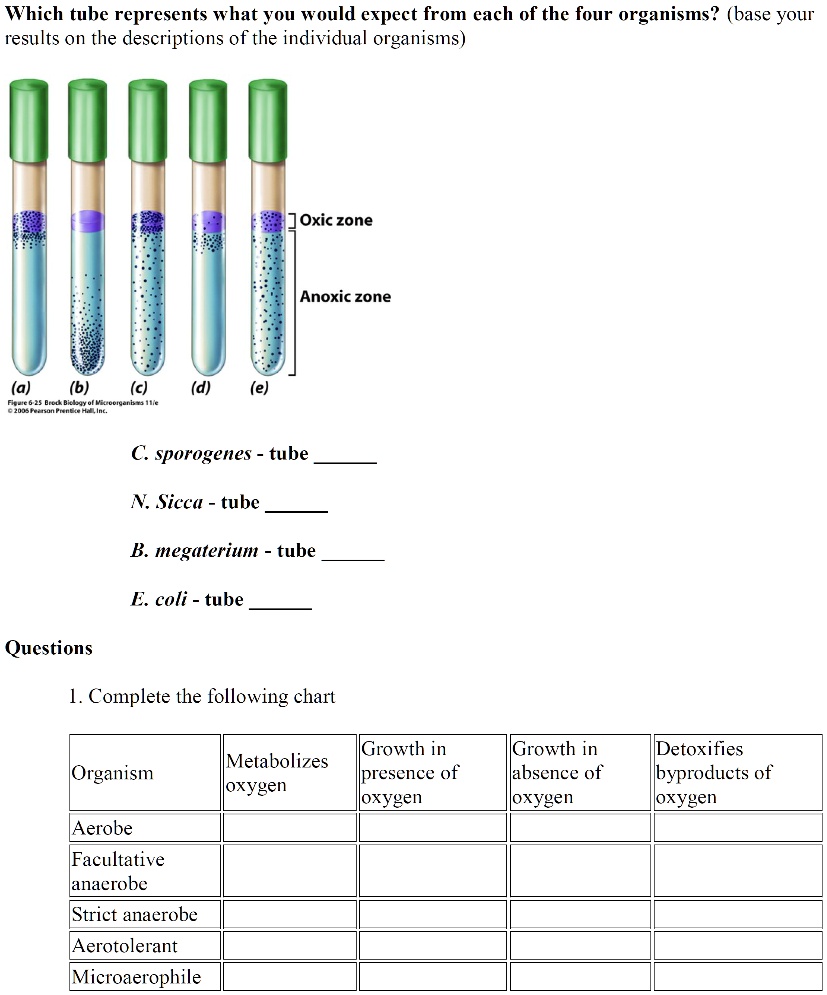
Facultative aerobes will grow either aerobically or in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic conditions), but they generally do better with oxygen. Aerotolerant.
E. coli is a facultative aerobe that would normally switch to anaerobic metabolisms at 0.005–0.02 PAL (1–4 μM O 2 in solution) . To ensure aerobic growth.
Optimal growth conditions for E. coli are 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees Fahrenheit, aerobic (with oxygen), and a pH of 7. E. coli is a mesophile which means its.
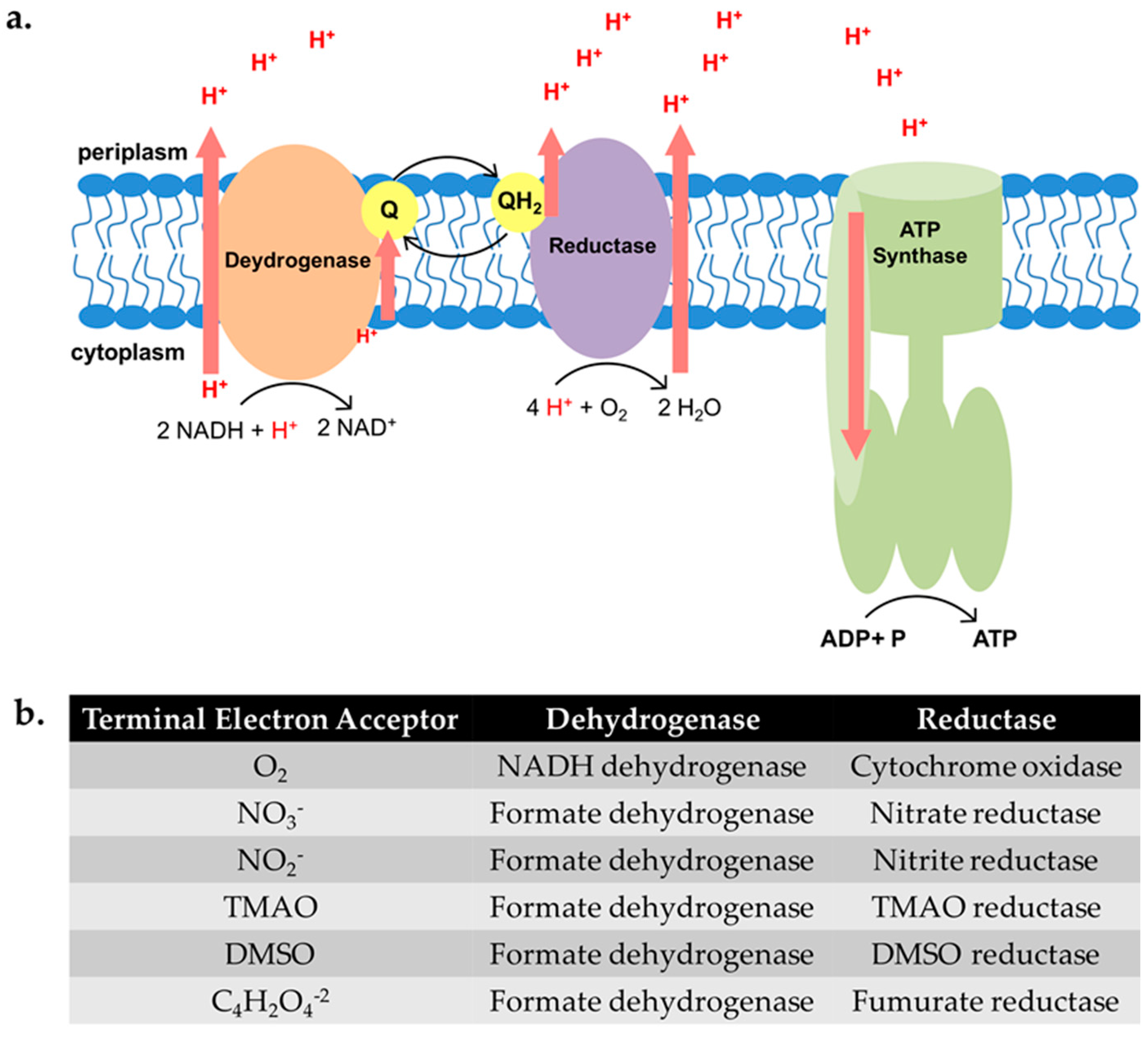
All three consumers of oxygen in E.coli are the oxidation of ubiquinone by at two sites in cytochrome- bcl or by cytochrome- bo. All of these export protons to create the gradient.
E. coli is able to grow aerobically by respiration and in the absence of O2 by anaerobic respiration with nitrate, nitrite, fumarate, dimethylsul.. In facultatively.
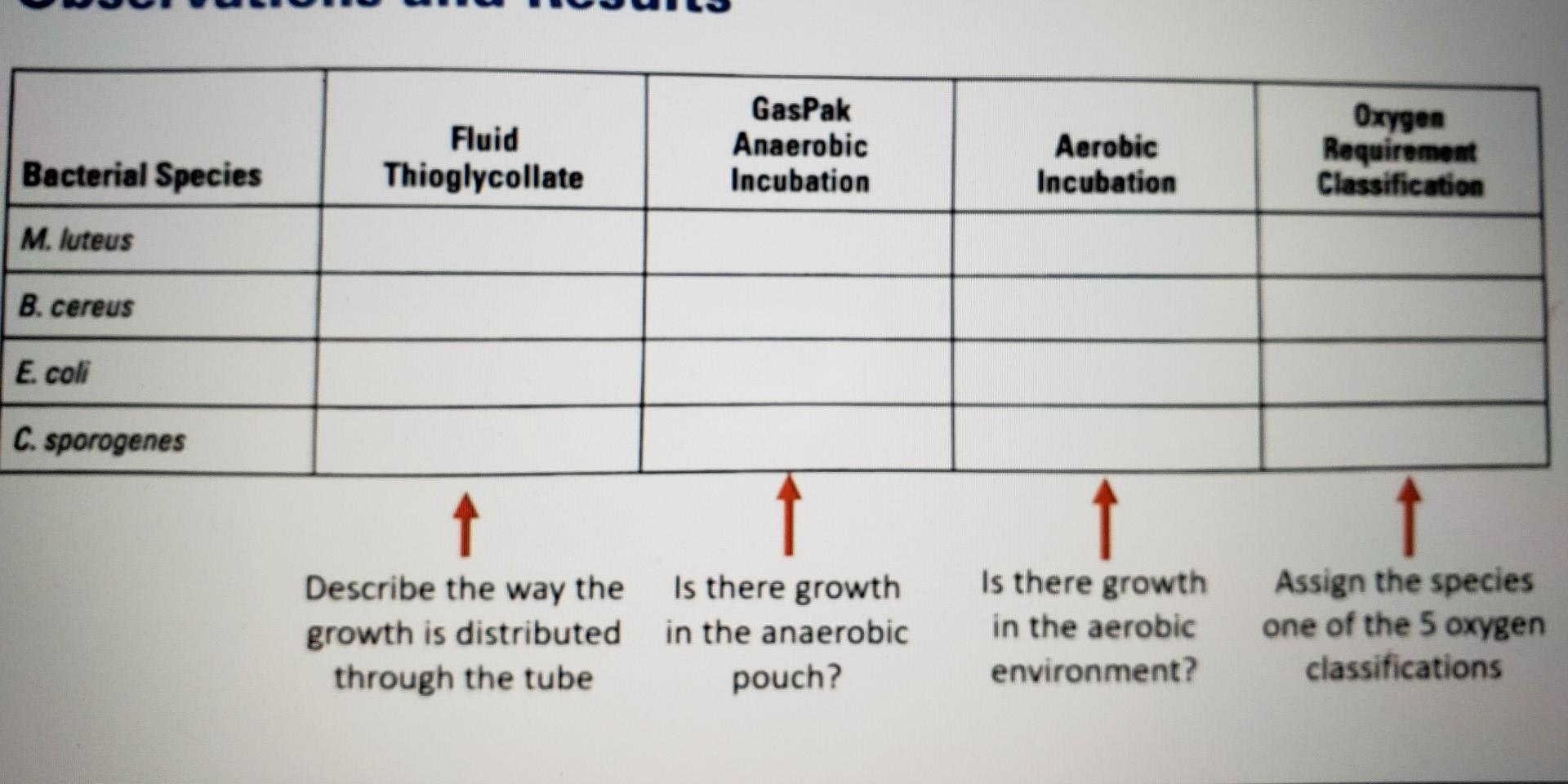
What are the 3 types of oxygen requirements in bacteria? Obligate Aerobes: oxygen required. Facultative: grow in the presence or absence of oxygen. Microaerophilic: grow.
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacteria that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E.coli strains are harmless, but some can.
Capnophilic (or carbon dioxide–loving) bacteria require increased concentration of carbon dioxide (5% – 10%) and approximately 15% oxygen. This condition can be.
E. Coli and oxygen: a motility transition. The motility of Escherichia coli is correlated with oxygen concentration. We show that oxygen penetrating into an.