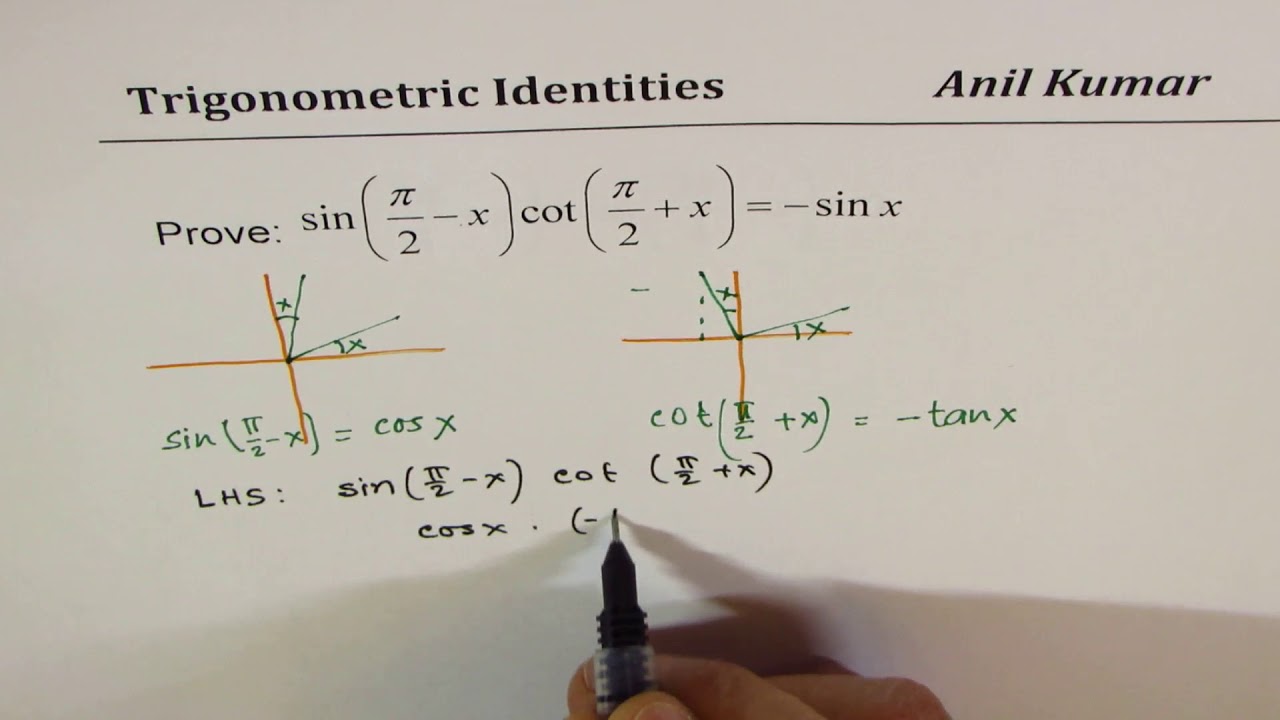
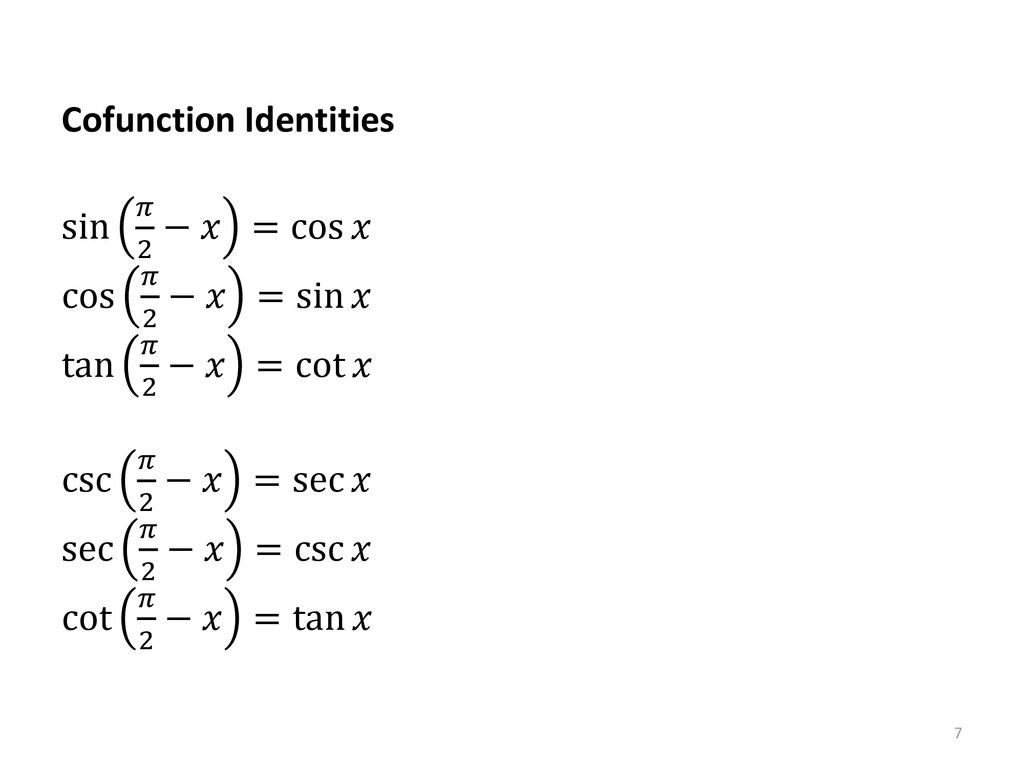
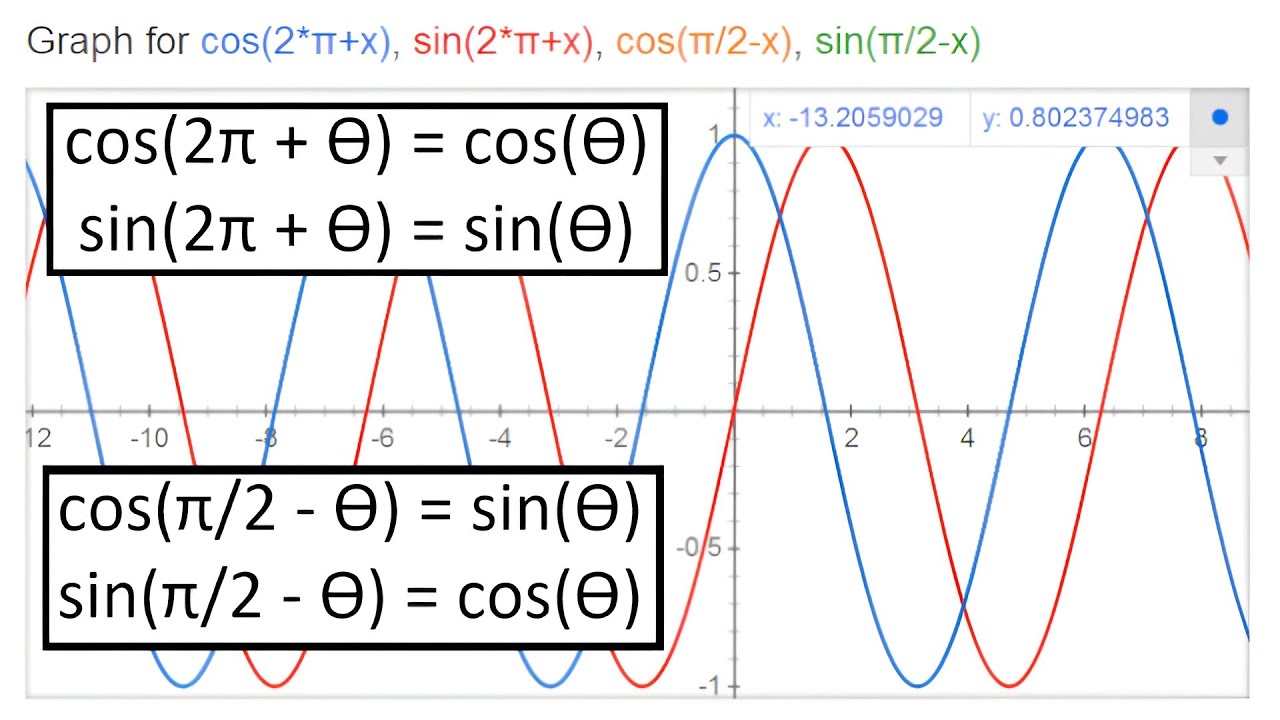
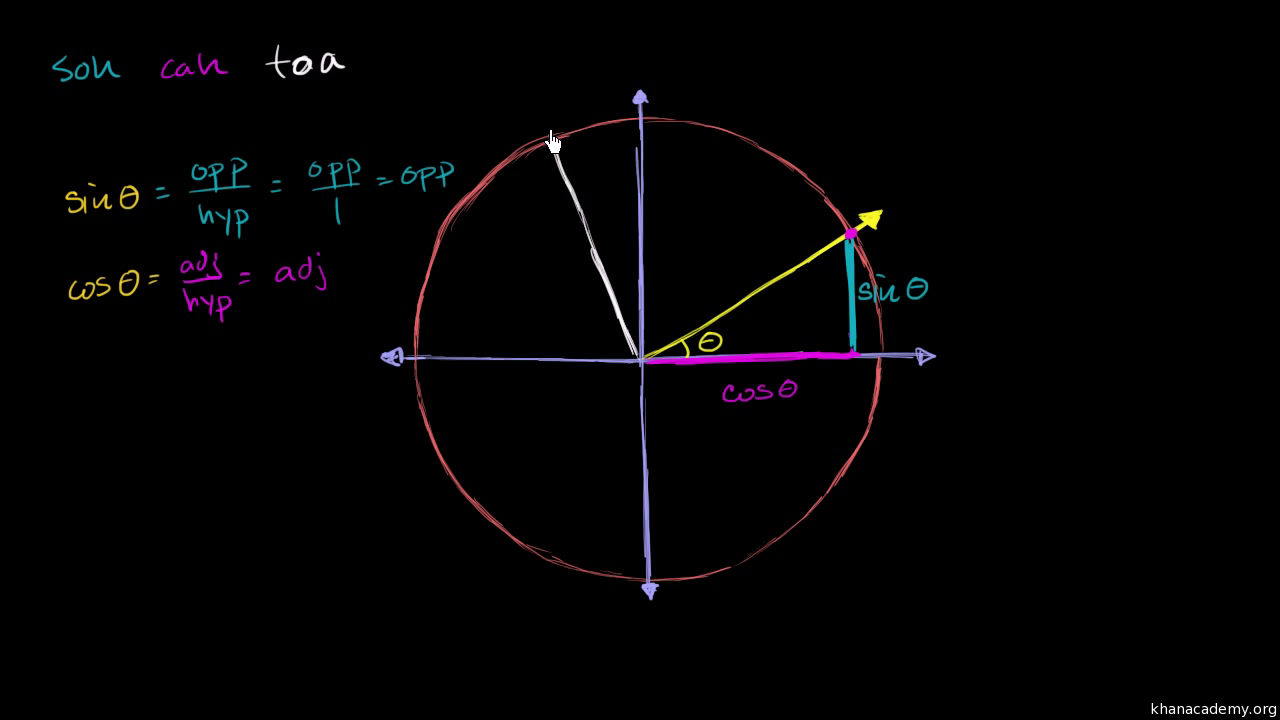
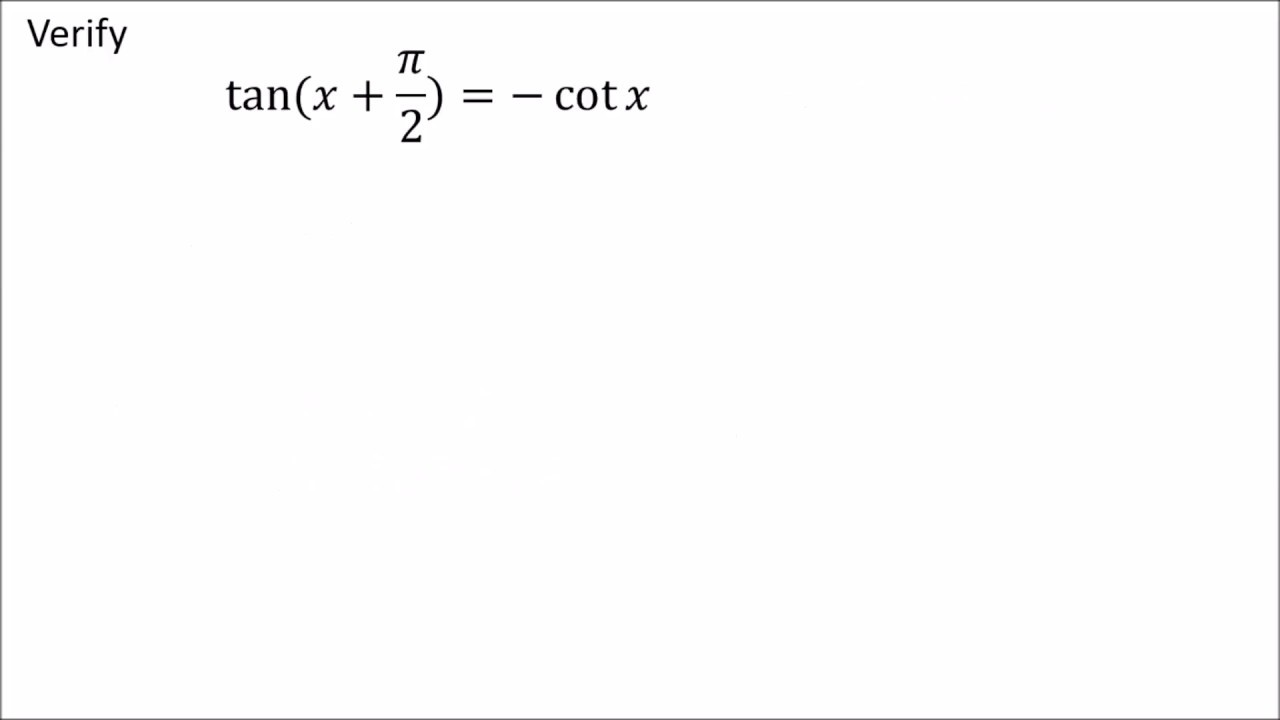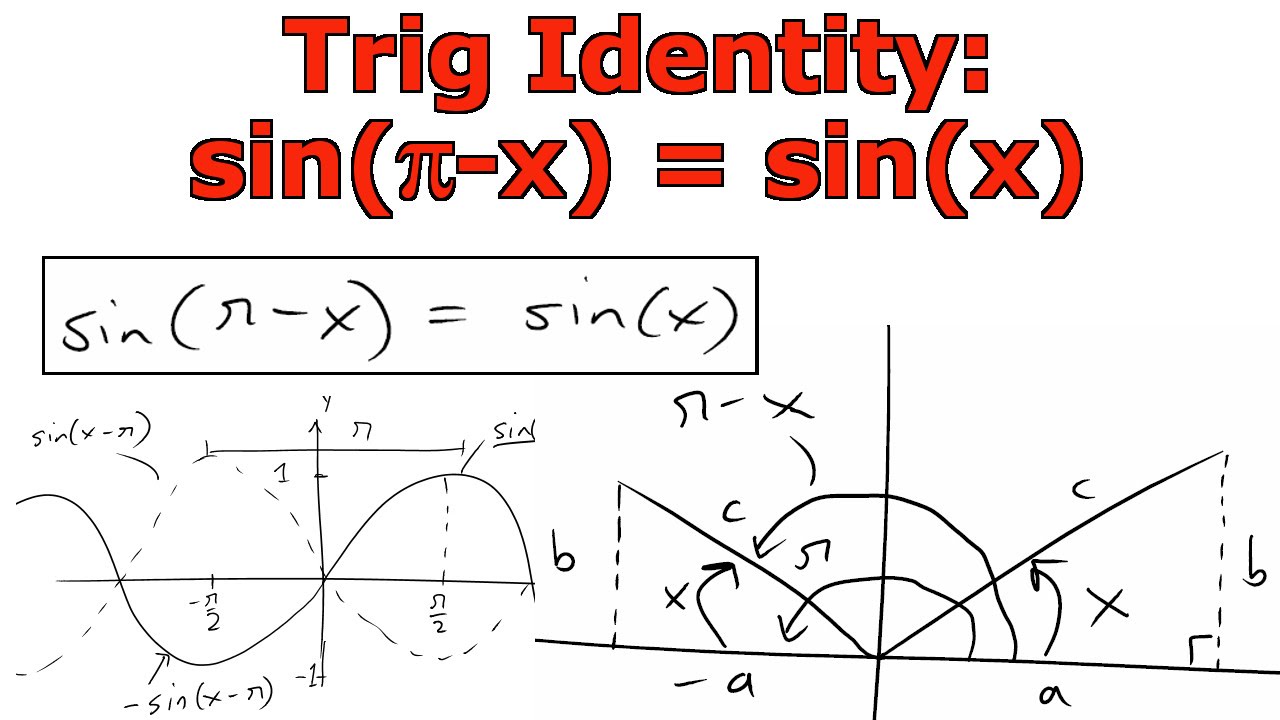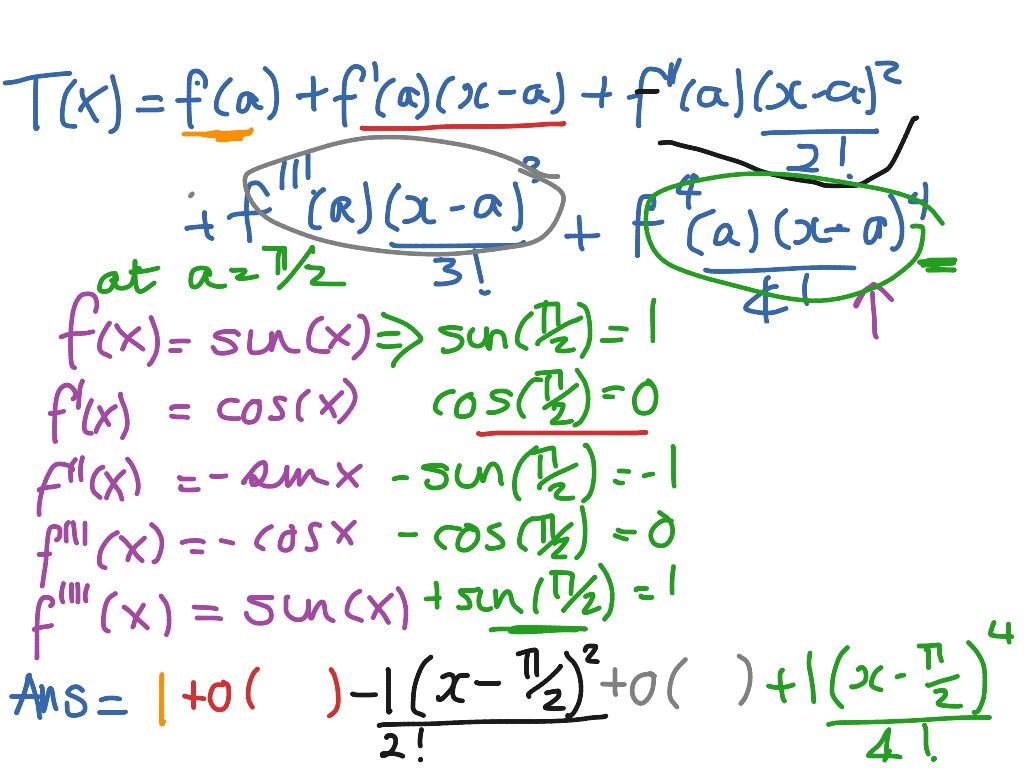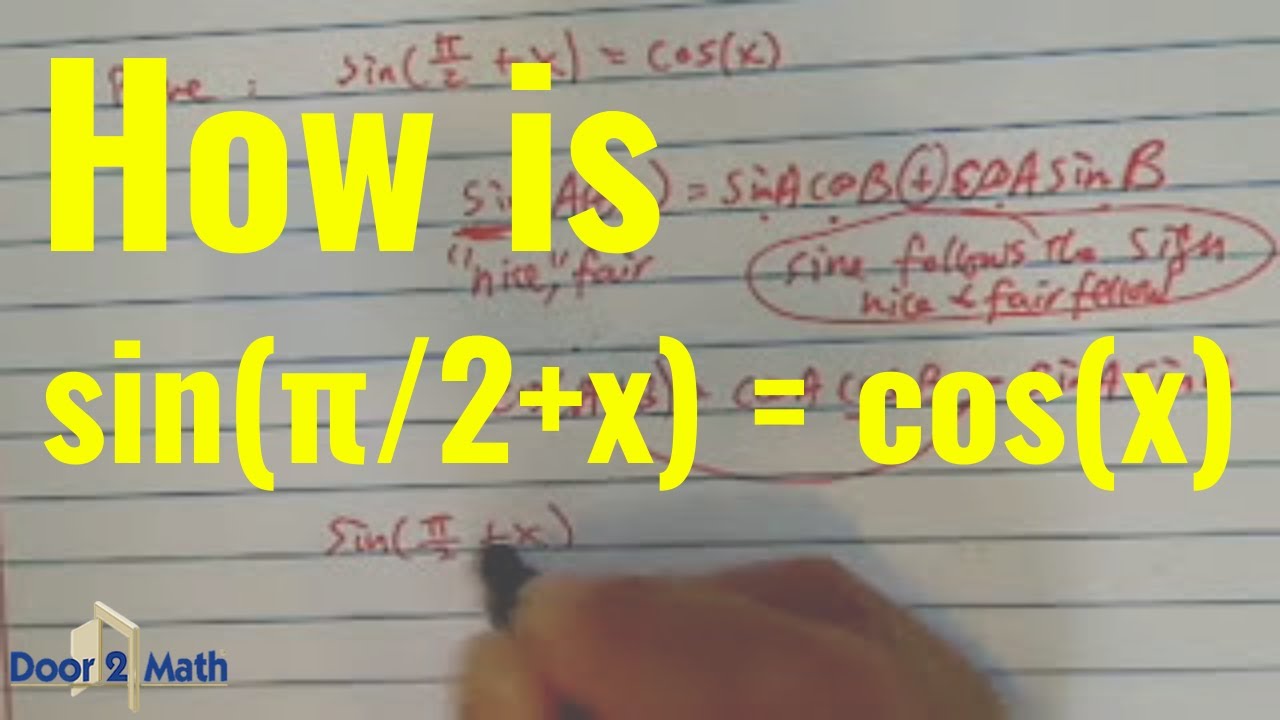USEFUL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES De nitions tanx= sinx cosx secx= 1 cosx cosecx= 1 sinx cotx= 1 tanx Fundamental trig identity (cosx)2 +(sinx)2 = 1 1+(tanx)2 = (secx)2.
Prove the identity. Sin (pi - x)/sin (x + pi/2) = tan x Note that each Statement must be based on a mark. This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject.
Expand the Trigonometric Expression sin (x-pi) | Mathway Trigonometry Examples Popular Problems Trigonometry Expand the Trigonometric Expression sin (x-pi) sin(x − π) sin ( x.
Prove the Identity. sin (x - pi/2) = -cos (x) Use the Subtraction Formula for Sine, and then simplify. sin (x - pi/2) = (sin (x)) (cos (pi/2)) - (cos (x)) (sin (x)) (0) - (cos (x)) Previous.
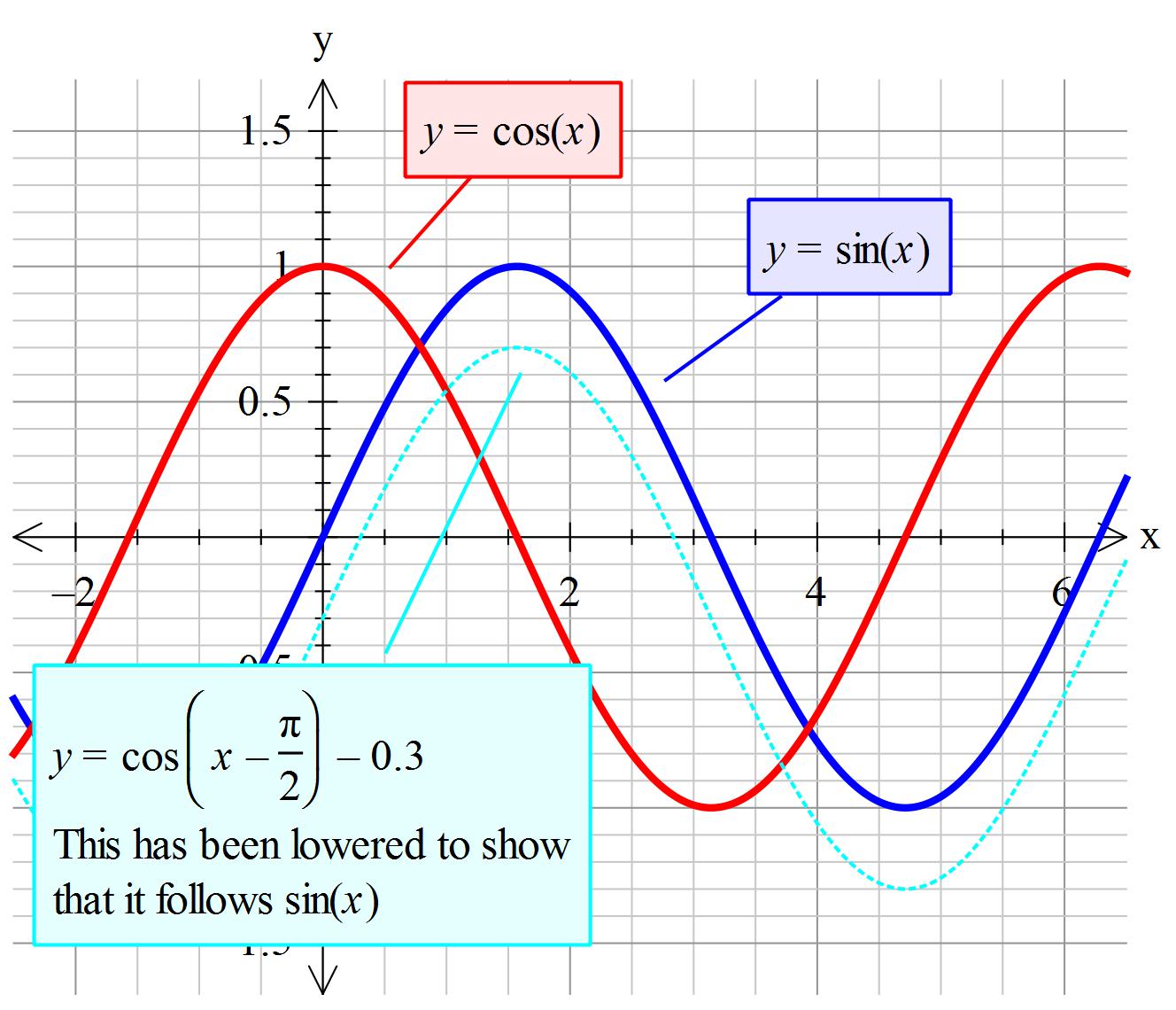
sin(x − π 2) is just sinx translated by ( π 2,0) We see that sinx: graph {sinx [-4.006, 4.006, -2.003, 2.003]} ∴ sin(x − π 2): graph {sin (x- pi/2) [-4.006, 4.006, -2.003,.
There is a group of Trig Identities that contain: cos(A-B)=cos(A)cos(B)+sin(A)sin(B) For your question this translates to: cos(x.
sin( π 2 + x) = cos(x) Since this answer is very usefull for student here the full demonstration to obtain sin(a + b) = sin(a)cos(b) +cos(a)sin(b) (do not read this if you are.
Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities and Equations Proving Identities 1 Answer Aviv S. Apr 7, 2018 Use the sine angle sum formula: sin(A +B) = sinAcosB +.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.