Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacteria that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E.coli strains are harmless, but.
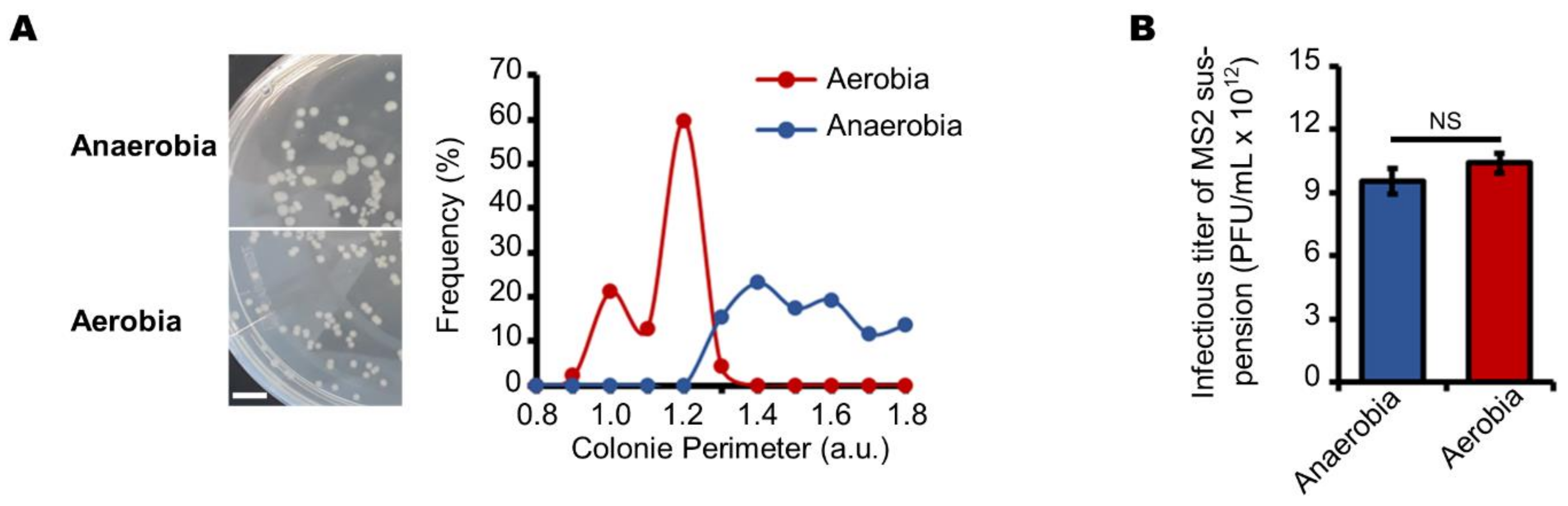
Here, a multi-level analysis of the aerobic respiratory chain of E. coli was performed to find correlations between gene transcription, enzyme activity, growth dynamics, and.
E. coli is a Gram negative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacteria of the genus Escherichia, commonly found in the lower intestine of humans and animals. Most.
Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria normally live in the intestines of healthy people and animals. Most types of E. coli are harmless or cause relatively brief diarrhea..
Les suspensions de bactéries lavées, provenant d'une culture de E. coli faite en aérobiose forcée, fermentent le glucose sans dégagement d'anhydride carbonique et.
Understanding life at a systems level is a major aim of biology. The bacterium Escherichia coli offers one of the best opportunities to achieve this goal. It is a.
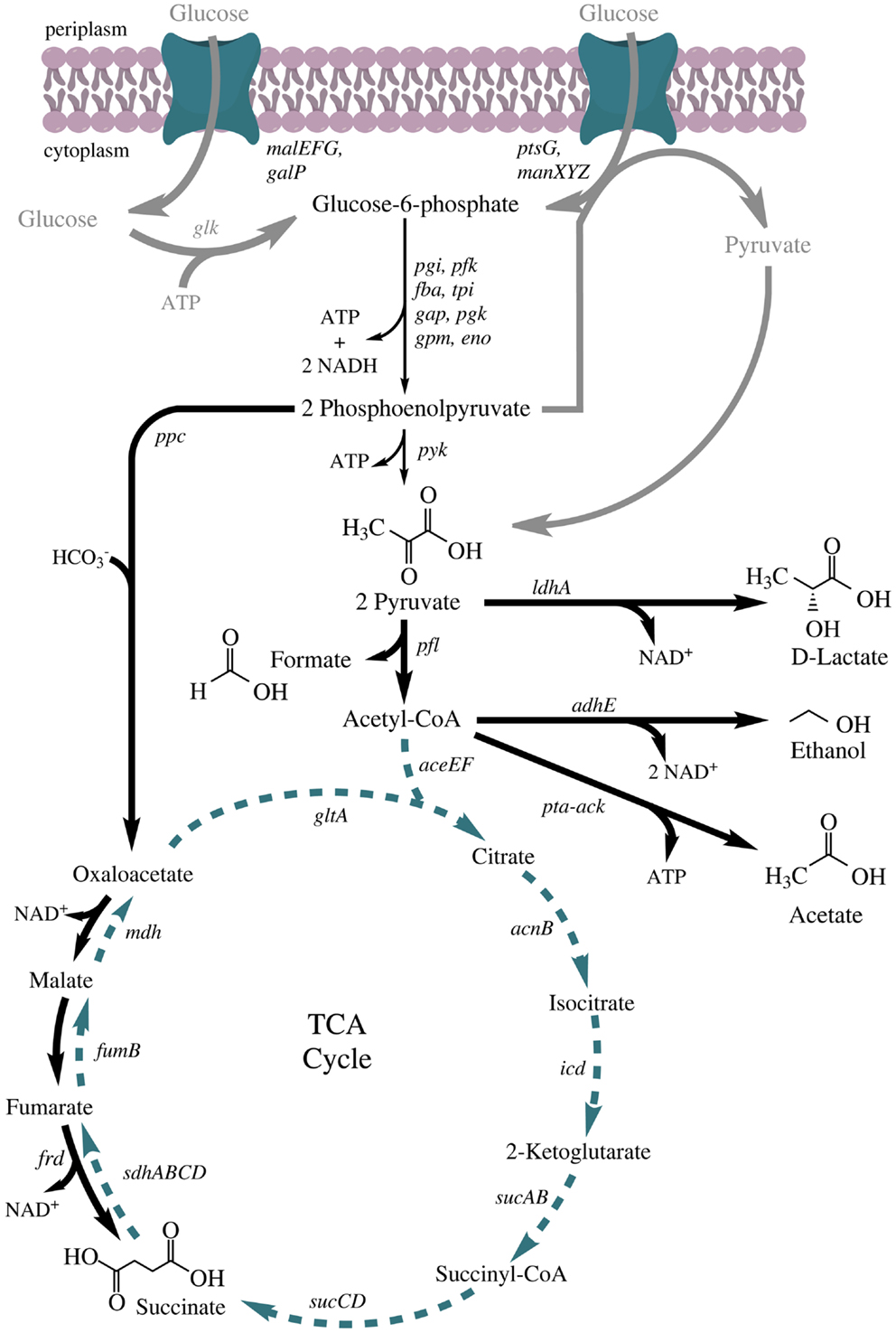
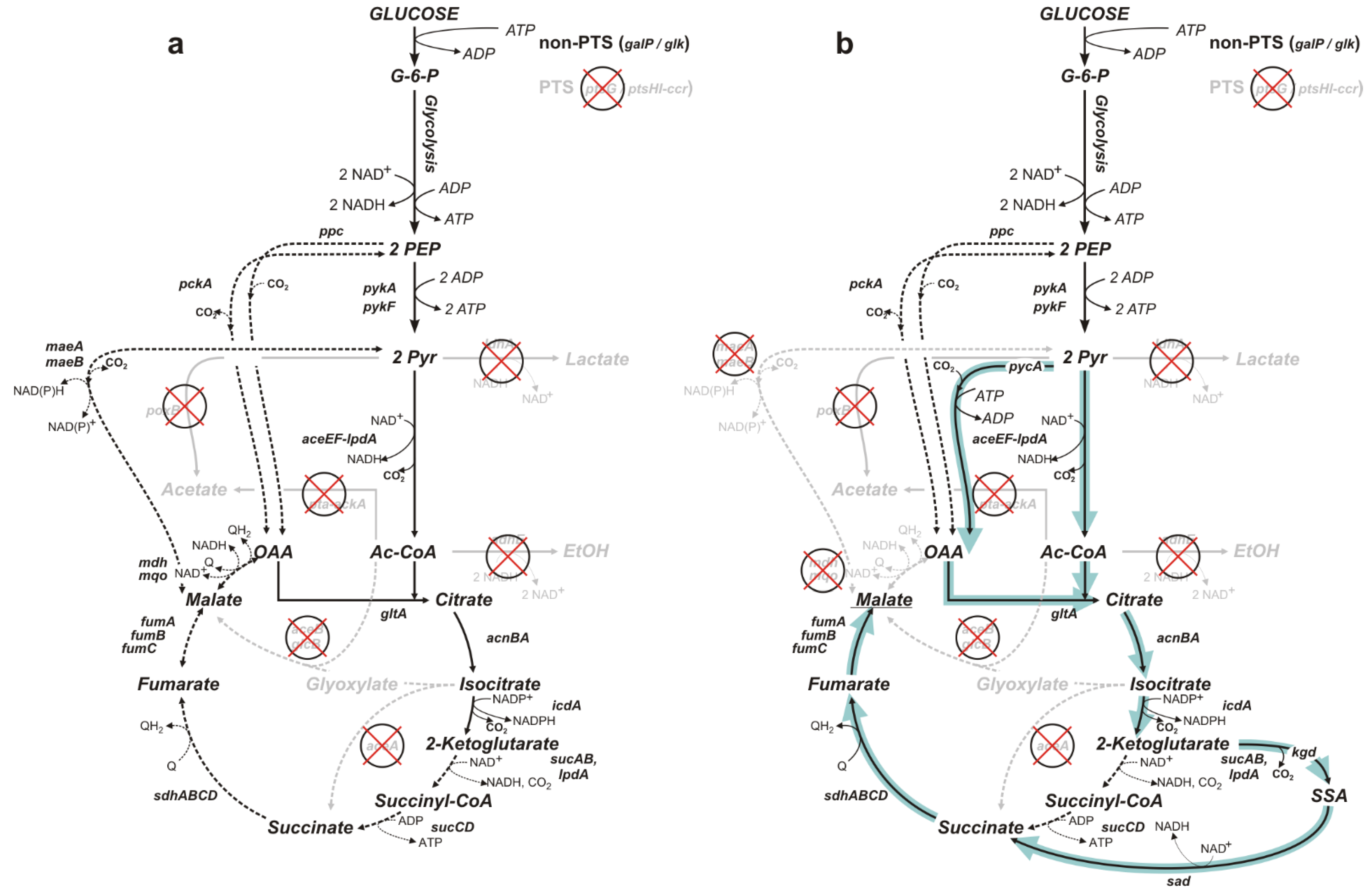
Escherichia coli is a metabolically versatile bacterium. In the presence of oxygen, it grows by aerobic respiration. When growing on glucose, it can completely.
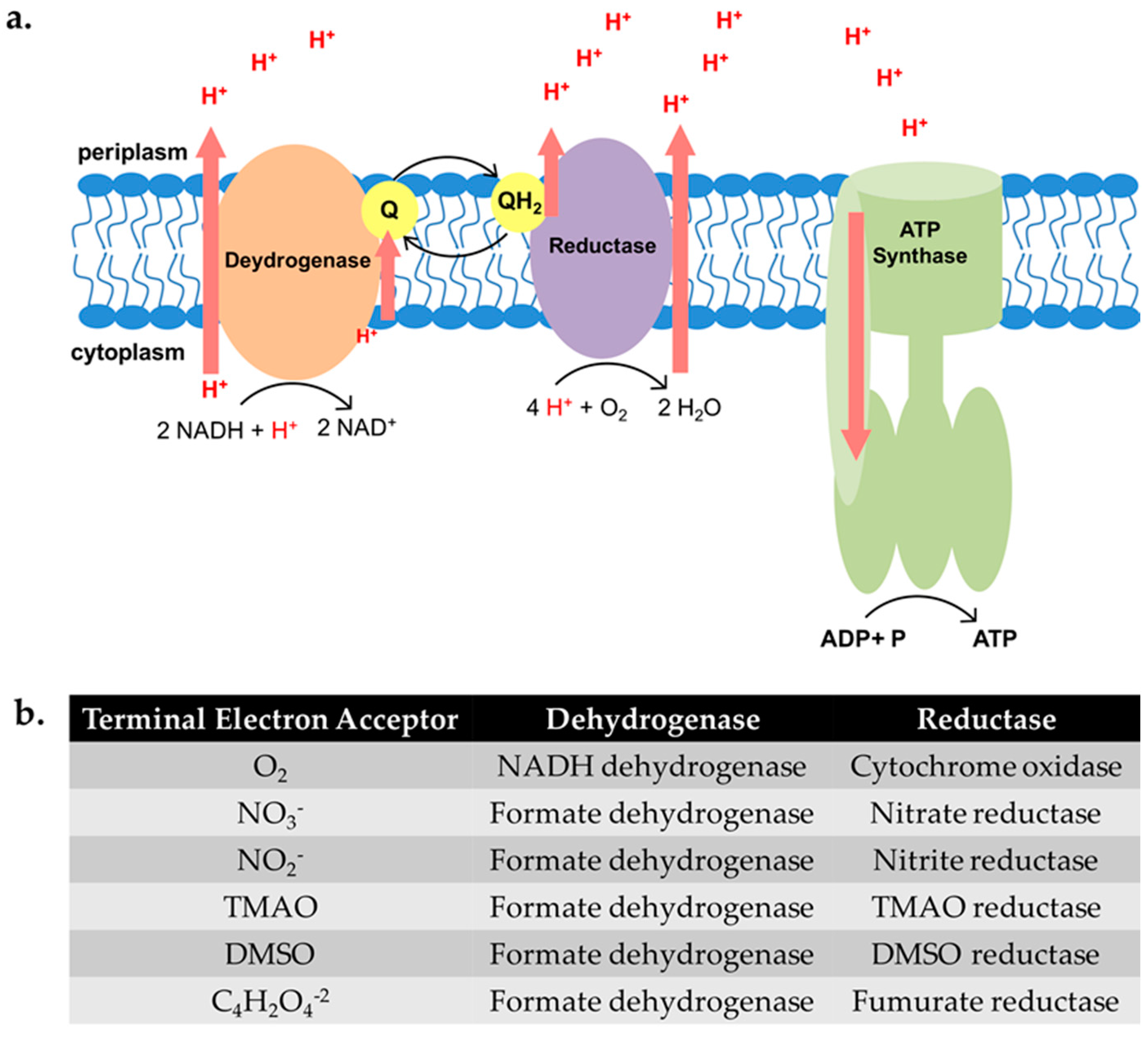
E. coli is able to grow aerobically by respiration and in the absence of O2 by anaerobic respiration with nitrate, nitrite, fumarate, dimethylsulfoxide and trimethylamine N-oxide as.
The aerobic respiratory chain of E. coli contains three enzymes that are known to generate a proton motive force: (i) the proton-pumping NADH:quinone.
$\begingroup$ E. Coli is not simply aerobic. Nor is it anaerobic. It is facultative, meaning that it thrives in both environments, and can breath with or without oxygen. Nor is it.
Abstract. Escherichia coli contains a versatile respiratory chain which oxidizes ten different electron donor substrates and transfers the electrons to terminal reductases or oxidases.
Some kinds of E. coli can cause diarrhea, while others cause urinary tract infections, respiratory illness and pneumonia, and other illnesses. Still other kinds of E. coli are.